Static electricity is a common phenomenon that occurs when two objects come into contact and then separate, resulting in an imbalance of electrons that generates a charge. This charge can create an electric field, and understanding the strength and potential of this field is crucial for various industrial applications.
Electric Field Strength
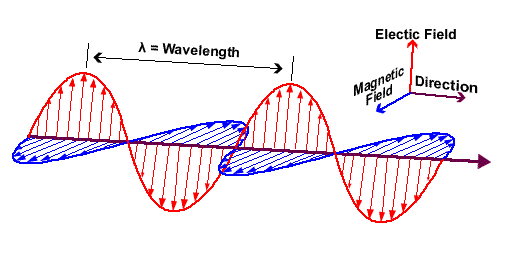
The strength of an electric field is measured by the force acting on a unit of charge (Coulomb) within the field. This is known as the electric field strength, and it is represented by the symbol E. The electric field strength is dependent on the distance between the charged objects and the magnitude of the charge. The unit of electric field strength is volts per meter (V/m).
Electric field strength is an important factor in various industries such as electronics, where it can cause issues such as equipment failure and product contamination. For example, in the semiconductor industry, the electric field strength can affect the performance of electronic components, and therefore, it is crucial to maintain a controlled environment with a low electric field strength.
Static Electric Voltage & Potential Equipment
Static electric voltage, also known as the static electric potential, is the difference in electric potential energy between two charged objects. This potential difference is measured in volts and is represented by the symbol V. The static electric potential is an important factor in various industrial applications, including electrostatic discharge (ESD) prevention and the design of high-voltage equipment.
Static electric potential equipment includes various devices that are used to measure, control, and prevent static electricity in industrial processes. These devices include static eliminators, ionizers, and grounding systems.
Static eliminators are devices that are used to neutralize static charges on surfaces. They work by emitting ions that neutralize any static charges on the surface, preventing the buildup of static electricity. Ionizers are similar to static eliminators in that they emit ions, but they are used to neutralize static charges in the air. Ionizers are commonly used in cleanroom environments where the buildup of static electricity can cause issues such as product contamination.
Grounding systems are used to prevent the buildup of static electricity on surfaces. They work by providing a path for the static charge to flow to the ground, thereby neutralizing the charge. Grounding systems are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, where the buildup of static electricity can cause explosions.
On the whole, static electricity is a common phenomenon that occurs when two objects come into contact and then separate, resulting in an imbalance of electrons that can generate a charge and an electric field. Understanding the strength and potential of this field is crucial for various industrial applications, including electronics, semiconductor manufacturing, and oil and gas industries. Static electric potential equipment, such as static eliminators, ionizers, and grounding systems, is used to measure, control, and prevent the buildup of static electricity in various industrial processes. By understanding and controlling static electricity, industries can improve efficiency, prevent equipment failure, and ensure the safety of their workers.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!